|
Time: 15 mins.
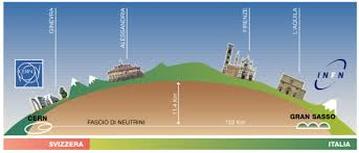
Task: In 2011, a group of scientists claimed that they had discovered that neutrinos (a type of sub-atomic particle) travelled faster that the speed of light between CERN and the Gran Sasso laboratory as shown in the diagram (Ruyet, 2011). Read this article and answer the questions below: |
- How many times did the group repeat the process?
- Was the error "random" or "systematic"? Explain your answer?
- Which parts of the scientific method ensured that these results were not published as an official discovery?
Extension: How was the cold fusion "discovery" in 1989 similar to this?
References:
Ruyet, D. (2011). Einstein, Steve Jobs, los neutrinos y el cambio renovador. El blog de David Ruyet. Retrieved 16 January 2016, from https://davidruyet.wordpress.com/2011/10/13/einstein-steve-jobs-los-neutrinos-y-el-cambio-renovador/
Ruyet, D. (2011). Einstein, Steve Jobs, los neutrinos y el cambio renovador. El blog de David Ruyet. Retrieved 16 January 2016, from https://davidruyet.wordpress.com/2011/10/13/einstein-steve-jobs-los-neutrinos-y-el-cambio-renovador/
Time: 30 mins.
Task: One surprising study in the UK has shown that wearing a bike helmet might actually be more dangerous for cyclists.
- Consider a possible hypotheses for this correlation.
- Design a simple investigation to test this hypothesis.
- State some control variables that would need to be considered.
Reference:
Bike crash. (2016). Upload.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 29 June 2016, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b0/MTB_over_the_bar_crash.jpg/1280px-MTB_over_the_bar_crash.jpg
Bike crash. (2016). Upload.wikimedia.org. Retrieved 29 June 2016, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b0/MTB_over_the_bar_crash.jpg/1280px-MTB_over_the_bar_crash.jpg