Activity 1 - Precision in scienceTime: 30 min.
Task: Much of the work we do in IB chemistry is based on using constants such as Avogadro's constant (NA), the gas constant (R) and the speed of light (c), but we rarely consider the precision or uncertainties in the values we use. Try tasks A and B below. |
|
Task A - Precision in a calculated value
i. Consider the three values to the right and identify which of them is the most precise. How do you know? ii. Why has the IB chosen a value with only 2 decimal places when there are more precise values available? (you might consider the precision of lab measurements to which we then utilise Avogadro's constant) |
Task B - Precision in measurement
|
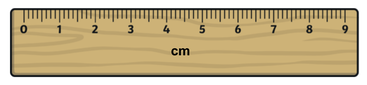
Experimentally defining an accurate and precise value of Avogadro's constant is a very challenging process as all experimental measurements have some degree of uncertainty. Two of the measurements required in this process are measuring the diameter of a silicon sphere and also its mass.
i. What would be the absolute uncertainty (+/-) in measurements made using the ruler and balance shown in the images? |
ii. Use your answer to part i to calculate the % uncertainty of a 3.65 cm measurement and a 4.81 g measurement.
iii. Assuming that the piece of silicone was a cube (volume = width x depth x height). Calculate the density of the silicon using the two values in part ii.
iv. Calculate the total % uncertainty in the density of the cube by propagating the % uncertainty of each measurement through your calculations.
iv. Calculate the total % uncertainty in the density of the cube by propagating the % uncertainty of each measurement through your calculations.
Task C - How did the National Institute of Standards and Technology calculate Avogadro's constant in 2018?
- Read this article about the level of precision required - Redefining the mole.
- Can you suggest examples of how they minimised uncertainty in their calculated values?