Activity 1 - The limitations of models
Subtopic 15.1 - Energy cycles
NOS statement 1.10 - Models tested against experiments or data from observations may prove inadequate
Time: 5 min.
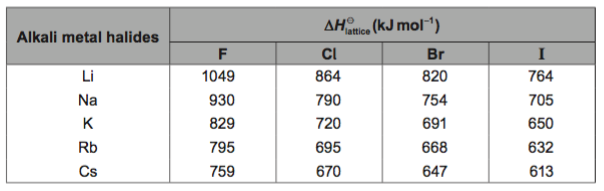
Task: Lattice enthalpy values calculated from Born-Haber cycles are based on the "ionic model" which treats ionic compounds as containing 100 % ionic bonding.
a. Compare and explain the values for lithium iodide and sodium iodide.
b. Compare the values for sodium iodide and silver iodide.
c. Given that the ionic radii for Na+ is 102 pm and Ag+ is 115 pm, what problems presents itself in the comparison made in b.?
d. Can you suggest an explanation?
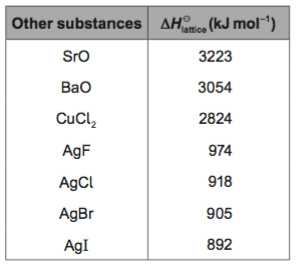
Task: Lattice enthalpy values calculated from Born-Haber cycles are based on the "ionic model" which treats ionic compounds as containing 100 % ionic bonding.
a. Compare and explain the values for lithium iodide and sodium iodide.
b. Compare the values for sodium iodide and silver iodide.
c. Given that the ionic radii for Na+ is 102 pm and Ag+ is 115 pm, what problems presents itself in the comparison made in b.?
d. Can you suggest an explanation?
Activity 2 - Accuracy and Hess's Law
Subtopic 15.1 - Energy cycles
NOS statement 2.4 - Laws are descriptive, normative statements derived from observations of regular patterns of behaviour. They are generally mathematical in form and can be used to calculate outcomes and to make predictions.
|
Time: 5 min.
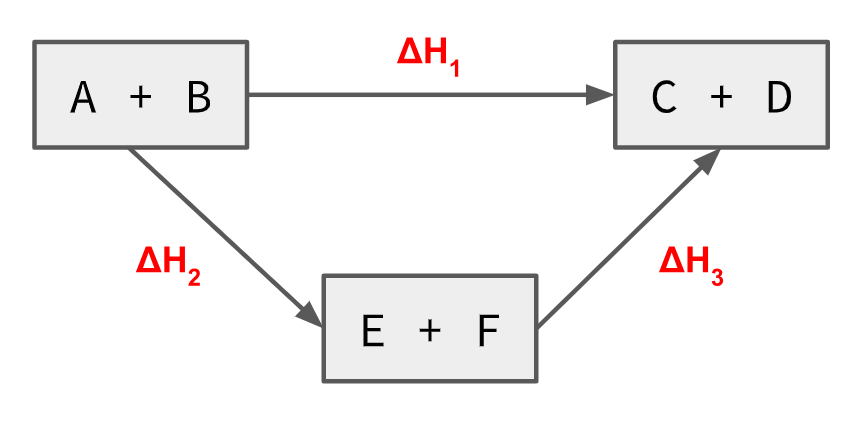
Task: True or false? 1. Hess's law is an application of the law of the conservation of energy. 2. Experimentally, DeltaH1 will be exactly the same as DeltaH2+DeltaH3. 3. Experimental uncertainty may affect the accuracy of using Hess's law. 4. The number of reactions used in an indirect pathway would decrease the total % uncertainty in the process. 5. The data found in the data booklet has no uncertainty. 6. Data in the data booklet is exactly the same as other literature sources. 7. A scientific law can be disproven. |